Classification and application of power transformers
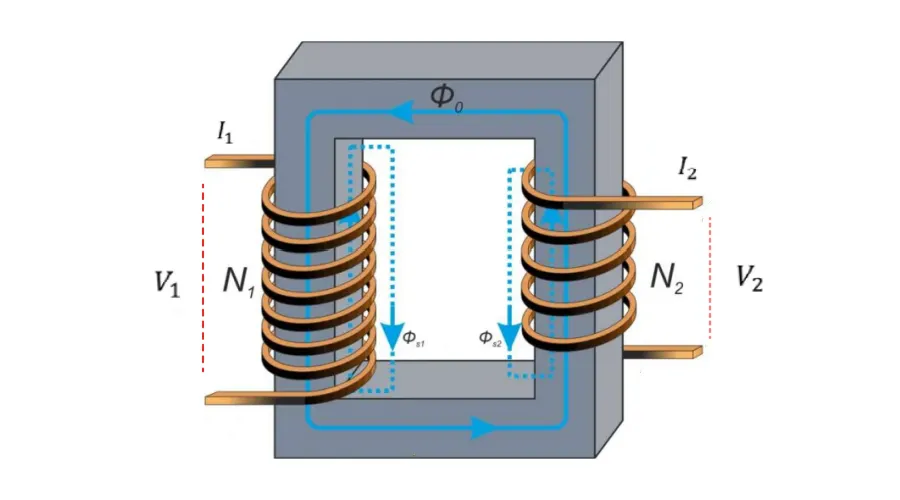
A transformer is an electrical device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to transfer electricity between circuits. It usually consists of two or more coils wound on a magnetic core. When alternating current passes through the primary coil, a changing magnetic field is produced, which is transmitted through the magnetoconductor to the secondary coil, inducing a voltage in it. This process enables voltage conversion, circuit isolation and impedance matching, widely used in electrical systems.
Types of transformers according to different categories:
Basic functions and applications of transformers
Transformers perform several key functions in electrical systems, among them:
- Voltage and current regulation: A transformer changes the voltage level in a circuit, which in turn affects the current. Increasing the voltage reduces the current and vice versa. This allows efficient transmission of electrical energy and minimizes losses during the transformation process.
- Electrical insulation: One of the most important tasks of a transformer is to isolate two electrical circuits. This prevents short circuits and protects the equipment from damage.
- Preventing DC transmission: The transformer blocks DC current, allowing only AC current to be transmitted. This protects devices designed for AC operation only.
- Adjustment of electrical characteristics: In some cases, transformers can change parameters such as capacitance, inductance or resistance in an electrical circuit, allowing the system to be adapted to different needs.
- Voltage rise and fall: The main purpose of transformers is to change the voltage level, which is necessary for appropriate conditions for the transmission and utilization of energy.
In addition, transformers are widely used in the following applications:
- Voltage increase on the generation side: Transformers increase the voltage on the generation side before transmitting electricity through the grid to reduce power losses over long distances.
- Voltage reduction for domestic and commercial use: Transformers reduce voltage, for example from 11 kV to 220 V single-phase and 440 V three-phase current, to adapt electrical energy for everyday use.
- Optimization of energy efficiency: Thanks to their ability to transform voltage, transformers help to increase the efficiency of power transmission and reduce losses, ensuring the stability of electrical networks.
Transformers play an indispensable role in electrical systems, providing reliable and efficient power transmission in a variety of applications, from industrial facilities to home and commercial needs.
Transformer types by purpose (including Russia, Kazakhstan and other CIS countries)
Transformers play a crucial role in power systems around the world, especially in countries such as Russia, Kazakhstan, Belarus and other Central Asian countries where they are an important part of power transmission and distribution as well as industrial applications. Depending on the application, transformers are categorized into several types, each with unique characteristics that meet different technical requirements. Here are the main types of transformers:
1. Power transformers
Power transformers are commonly used for long-distance transmission of electricity, playing an important role in converting high-voltage electricity generated in power plants into low-frequency current suitable for long-distance transmission. These transformers are critical in Russia, Kazakhstan and other CIS countries, where they ensure safe and efficient transmission of electricity from power plants to substations and end consumers.
Power transformers are usually oil-filled, with solid insulation and an efficient cooling system. In Russia and other CIS countries, typical rated voltages for these transformers are 110 kV, 220 kV, 330 kV, 500 kV, etc., which facilitates efficient transmission of electricity over long distances. For example, in Kazakhstan, power transformers play an important role in interstate power transmission and supporting regional power grids.
The principle of operation of power transformers is to convert low-voltage current with high current into high-voltage current with lower current, which is necessary to minimize energy losses in distribution systems. In these countries, a three-phase AC system with a frequency of 50 Hz is most commonly used.
2. Distribution transformers
Distribution transformers play a key role in the process of delivering electricity from substations to end users, converting high voltage to the required voltage for use in homes and businesses. These transformers can be single-phase or three-phase.
In Russia, Kazakhstan and Belarus, distribution transformers can be installed in different ways, depending on the needs of the local network. For example, they can be installed on poles (so-called pole-mounted transformers) or in underground chambers. It is also possible to install transformers in enclosed steel cabinets. The rated voltages for these transformers are usually 220 V, 380 V, 660 V, depending on the needs of the end users.
Distribution transformers can also be dry-type or oil-type, depending on the type of insulation. Oil-filled transformers are widely used in these countries because of their reliability and efficiency at high loads, especially in remote areas and harsh climates.
3. Measuring transformers (Interphase transformers)
Measurement transformers (or measurement transformers) are commonly used to accurately measure current, voltage and power in electrical networks and to protect and monitor system operation. These transformers convert high voltages and currents into smaller voltages and currents suitable for use by measuring instruments.
In CIS countries such as Russia, Kazakhstan and Belarus, measuring transformers are widely used for monitoring and protection of electrical networks, as well as for precise measurements in power systems. Their rated currents typically range from 1 to 5 A and voltages from 100 V to 500 V, at a frequency of 50 Hz. These transformers play an important role in ensuring the safety and stability of power systems.
4. Transformers for inverters
Converter transformers are used in systems that convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) and vice versa. They are widely used in Russia and Kazakhstan in high-voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission systems, providing voltage conversion between different sections of the network.
The nominal voltage of these transformers often exceeds 110 kV and their power can reach several thousand kilovolt-amperes. These transformers are essential to ensure efficient and safe energy conversion in complex distribution networks, including international systems such as the transmission of energy between Russia and neighboring countries.
5. Special transformers
In Russia, Kazakhstan and other CIS countries, special transformers are also used for specific industry needs such as welding and powering electric furnaces. These transformers are typically high power and provide power for industrial devices.
Specialty transformers are used in industries such as metallurgy, chemical industry, and power generation to provide stable power supply for heavy industrial equipment. These countries are witnessing an increasing demand for such transformers in view of the development of various industries.
6. Transformers with natural air cooling
Free air-cooled transformers are gaining popularity in Russia and Kazakhstan due to their high energy efficiency and reduced size compared to traditional oil transformers. These transformers do not require oil for cooling and utilize new heat-resistant insulation materials to improve their performance.
These transformers typically range from 133 to 6300 kVA and are used to power large electrical installations such as turbine generators and electric drives. They are ideal for use in areas with harsh climatic conditions where cooling problems are common.
Evernew Transformer is a leading manufacturer of various types of transformers that are widely used in power and industrial systems in Russia, Kazakhstan and other CIS countries. The company specializes in the production of power, distribution, measuring transformers, as well as transformers for converters and specialized needs such as welding and powering electric furnaces. Due to high reliability and compliance with international standards such as GOST, UL and CE, Evernew Transformer transformers provide efficient and safe power transmission in various climatic conditions and for a wide range of industries including metallurgy, chemistry, power generation and others. The company also offers free air-cooled solutions ideal for use in areas with harsh climates and limited access to maintenance.
Application of oil transformers for energy storage










