Power transformers play a key role in the transmission and distribution of electric power. Their correct calculation determines the reliability of the power system, economic efficiency and the service life of the equipment. In this article we will look at how to determine the transformer capacity, calculate losses and estimate its efficiency.
1. Rated power of the transformer
Transformer power (S, kVA) indicates the electrical load it is capable of serving.
Formula for calculating the total power:
 where UU - Tension, II - current on the corresponding side of the transformer.
where UU - Tension, II - current on the corresponding side of the transformer.
The power rating is selected based on the required load with allowance (typically 20-30%).
2. Types of losses in transformer
During operation, some energy is inevitably lost. The main types of losses are:
Idle losses (P₀)
Occur in the magnetic core when voltage is applied without load.
Include hysteresis losses and eddy currents.
Load losses (Rk)
Related to the heating of the windings when current flows.
Depends on the winding resistance and the size of the load.
Active loss formula:
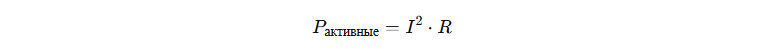
where RR - winding resistance, II - current.
3. Transformer efficiency
The efficiency factor (η) reflects the efficiency of the transformer.
Efficiency formula:
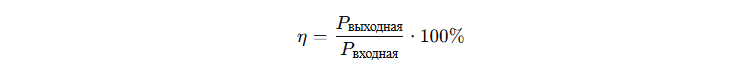
or loss-adjusted:
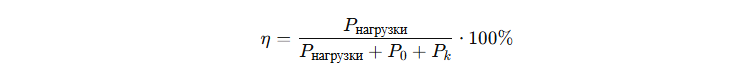
Modern power transformers can reach KPD 98-99%This reduces operating costs.
4. Calculation example
Let's say the transformer has:
Rated power: 1000 kVA
Idle losses: 2 kW
Load losses: 10 kW
Calculation of efficiency at full load:
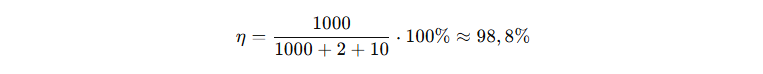

5. How to reduce losses and increase efficiency
Use of quality electrical steel in the magnetic core
Use of copper windings with minimum resistance
Efficient cooling (oil, air, combined)
Optimal selection of the load mode (avoid idling or overloading)
Conclusion
Correct calculation of transformer power, losses and efficiency allows:
choose the right equipment for the right task,
reduce operating costs,
to ensure the reliability of the power grid.
Knowledge of these basics is useful to both engineers and electrical procurement and operations professionals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
❓ What efficiency is considered normal for a modern power transformer?
➡ Usually in the range of 98-99%.
❓ Does temperature affect losses?
➡ Yes, as the temperature rises, the winding resistance increases, resulting in higher load losses.
❓ Can idle loss be eliminated completely?
➡ No, but they can be minimized by quality magnet core materials.
📌 power transformer, transformer power, transformer losses, transformer efficiency, transformer calculation, transformer efficiency


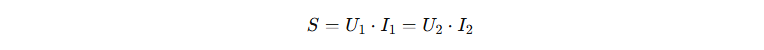 where
where