Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is an oil transformer?
Oil transformers are key devices in the energy infrastructure used for power conversion and distribution. Their main task is to smoothly reduce or increase the voltage in the network, ensuring a stable supply of energy to consumers. Their role is particularly important in long-distance power transmission systems, where transformers minimize losses and provide the required output voltage.
Oil transformers are widely used in various climatic conditions, including the extremely low temperatures typical of northern regions. This is achieved through the use of transformer oil, which not only serves as insulation, but also effectively cools the windings and magnetic conductor, preventing overheating. Such devices are highly reliable, resistant to temperature fluctuations and able to withstand overloads, making them indispensable in the energy industry.
Unlike dry-type transformers, oil-filled devices provide more efficient cooling and longer service life, making them the preferred choice for most industrial applications. The use of oil transformers also contributes to increased operational safety, which is particularly important for facilities requiring high reliability and long-term operation.
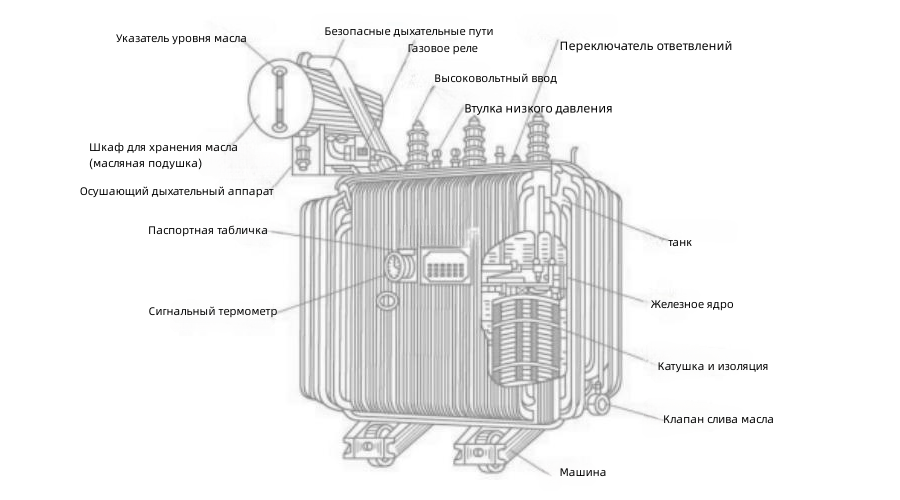
Design of the oil-filled power transformer
The design of oil-filled power transformers has much in common with other types of transformers, but includes several unique features related to the use of oil as a cooling and insulating agent. The main structural elements of the transformer are a magnet core made of ferromagnetic materials and windings made of copper or aluminum, which are cylindrical in shape.
The difference between an oil transformer and an oil transformer is the presence of a housing filled with transformer oil. The oil has two main functions: it serves as an insulator, preventing short circuits between the windings, and it effectively cools the transformer by absorbing the heat generated during operation. To compensate for changes in oil volume caused by temperature fluctuations, the transformer is equipped with a special expansion tank.
To monitor the temperature of the oil in the transformer, temperature sensors are installed on the tank lid as well as on the winding inlets and outlets. In addition, a special air dryer is used to prevent moisture and contaminants from getting inside the device, which significantly increases the durability and efficiency of the transformer.
The transformer housing is made of high-strength materials, which increases its resistance to external influences. Magnetic conductor made of electrotechnical steel improves the electromagnetic characteristics of the transformer, which contributes to its more efficient operation.
Transformer windingsmade of copper or aluminum, include conductors and various insulating components that protect the coils from external influences and mechanical damage. To protect the tank and ensure the safety of the unit, a special enclosure with emergency shutdown devices is used. The electrical circuit connects the windings to the transformer through the cover using bushings insulators.
To protect against unwanted gases and oil, the transformer enclosure has a ventilation system with a gas relay that monitors pressure changes inside the unit. Piping is also provided to vent harmful gases, which is controlled via a handle on the tank lid. The transformer cover is equipped with clamps and magnetic locks, which ensures tightness and safety of the device operation.
The design of oil transformers is focused on ensuring high operational reliability and safety, which is especially important in the power industry, where every element must operate smoothly for many years.
Oil transformer operation: principle and features
An oil transformer is a sealed device consisting of several windings placed in a tank filled with transformer oil. The oil not only serves as an insulator, but also has a cooling function. Before being filled into the transformer, the oil undergoes a degassing process to avoid air and moisture, which can affect its performance.
The basic principle of operation of an oil transformer is based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current is applied to the primary winding, a changing magnetic field is generated and transmitted through the magnetic conductor. This magnetic field induces a current in the secondary winding, creating a potential difference called secondary voltage. Energy is transferred from one winding to the next due to the electric field created by this changing magnetic flux.
One of the key features of an oil transformer is the use of transformer oil, which performs several important functions:
- Winding cooling - The oil absorbs the heat generated during operation of the unit, preventing overheating.
- Insulation - The oil serves as an insulator between the windings and the metal parts of the transformer, ensuring electrical safety.
- Diagnostic function - changes in the condition of the oil can serve as an indicator of the condition of the transformer. For example, the presence of contaminants or water in the oil can indicate possible problems with the device.
In addition, the oil plays an important role in maintaining stable operation of the transformer, ensuring its longevity and reliability. To ensure efficient heat transfer between the oil and the external environment, additional elements such as metal plates are included in the transformer design to increase the contact surface and speed up the cooling process.
Inside the tank, the oil moves through several circuits, which promotes its circulation and even temperature distribution. To monitor the oil temperature, temperature sensors are installed on the transformer. If the temperature exceeds the permissible limits, the system can automatically regulate the cooling processes or shut down the unit to prevent damage.
It is important to note that transformer oil is a flammable liquid and there are certain risks associated with the use of oil transformers. Therefore, such devices should be installed away from ignition sources and regularly checked for leaks or contamination to prevent possible accidents.
The oil transformer is an important element in the distribution of electricity, and its proper operation and maintenance is critical to the smooth operation of the electrical grid and safety in general.
Types of oil transformers
Oil transformers are divided into two types: TM (leaky) and TMG (hermetically sealed), differing in design and performance. The voltage of these transformers varies from 6(10) kV to 35 kV, depending on the model and purpose.
TM - leaky transformers. The oil in these units is in contact with the external environment via an expansion tank, which requires additional air drying equipment. These transformers are sensitive to temperature fluctuations and the oil in them needs to be changed and disposed of regularly. The voltage of these transformers is typically 6 (10) kV to 35 kV, which is suitable for medium and low power distribution and transformation.
TMG - hermetic transformers. The oil in these units does not come into contact with the outside environment due to the hermetically sealed shell, which minimizes the need for maintenance. These transformers are equipped with overpressure relief valves and are suitable for continuous operation without oil change. They also operate at 6 (10) kV up to 35 kV, offering high reliability and efficiency.
Oil transformers can be three-phase or single-phase, with capacities ranging from 10 to 1000 MVA. They can be used for both raisesand for downgrades voltages, providing versatility for different energy needs.
The choice of transformer type depends on the operating conditions, required power and voltage level. Sealed models offer lower maintenance requirements and longer life, while non-sealed models require closer monitoring of the oil condition.
Oil transformers have many advantages over dry-type transformers, which makes them one of the most popular types of equipment in power systems in Russia and worldwide. One of the key advantages of oil transformers is their ability to effectively protect windings from external negative influences and operate in the temperature range from -60°C to +40°C. This device has a low level of reactive power and high reliability, which significantly reduces the need for monitoring and maintenance.
Oil plays an important role in the transformer, providing both cooling and insulation. It prevents the windings from coming into contact with the outside environment, protecting them from moisture, oxidation and contamination, which greatly extends the life of the transformer. Oil transformers also have a lower cost than their dry-type counterparts, making them more affordable for a wide range of applications, including energy-intensive industries. Oil transformers are particularly effective in high-voltage applications such as 110 kV and 220 kV.
How to buy an oil transformer
Company Evernew Transformer is a leading manufacturer of oil transformersoffering a wide range of devices for various needs, including high voltage devices transformers with voltage up to 220 kV. We manufacture oil transformers with capacities ranging from 10 kVA to 1000 MVA to meet the requirements of a wide variety of industries and applications. Our transformers provide stable operation and high efficiency, even under the most demanding operating conditions.
Purchasing a transformer from the company Evernew Transformer easy and convenient. In order to choose the right model, all you need to do is fill out the questionnaire on our website. We offer individual consultations to help you choose the optimal solution, taking into account all technical parameters and operating features. Our team of experts guarantees that the purchased equipment will work smoothly for decades.
